Wen Liu | Cell Reports: Targeting PRMT1-mediated SRSF1 Methylation to Suppress Oncogenic Exon Inclusion Events and Breast Tumorigenesis
Highlights
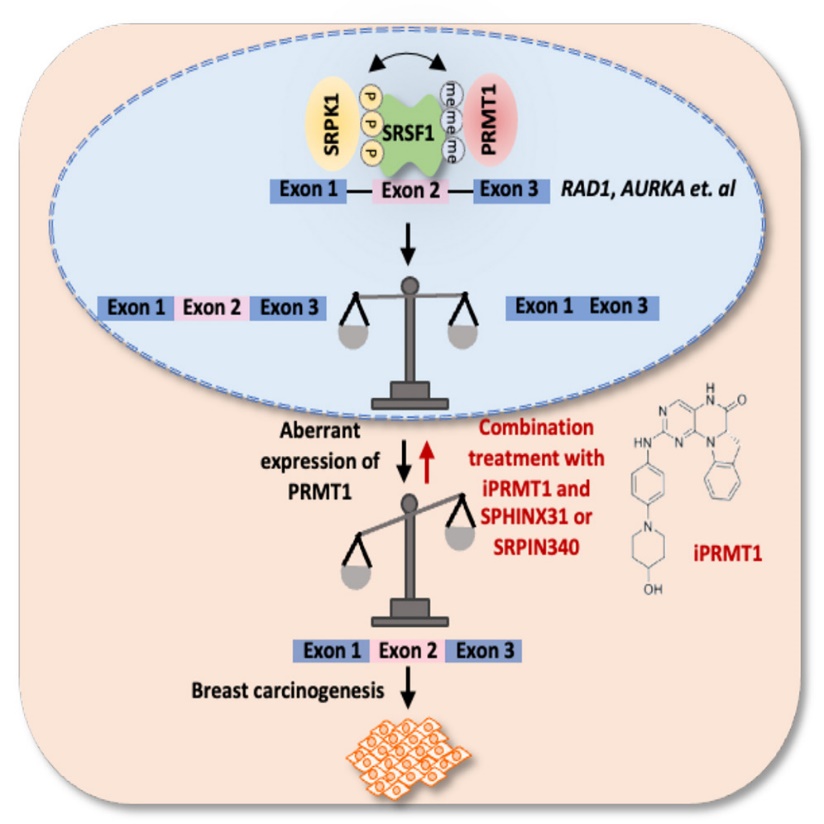
•PRMT1 induces exon inclusion in a number of oncogenes by methylating SRSF1
•SRSF1 methylation is critical for its phosphorylation and its binding with RNA
•PRMT1-induced exon inclusion promotes the malignant behaviors of breast cancer cells
•A PRMT1 inhibitor iPRMT1 inhibits breast cancer cell growth both in vitro and in vivo
Summary
PRMT1 plays a vital role in breast tumorigenesis; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Herein, we show that PRMT1 plays a critical role in RNA alternative splicing, with a preference for exon inclusion. PRMT1 methylome profiling identifies that PRMT1 methylates the splicing factor SRSF1, which is critical for SRSF1 phosphorylation, SRSF1 binding with RNA, and exon inclusion. In breast tumors, PRMT1 overexpression is associated with increased SRSF1 arginine methylation and aberrant exon inclusion, which are critical for breast cancer cell growth. In addition, we identify a selective PRMT1 inhibitor, iPRMT1, which potently inhibits PRMT1-mediated SRSF1 methylation, exon inclusion, and breast cancer cell growth. Combination treatment with iPRMT1 and inhibitors targeting SRSF1 phosphorylation exhibits an additive effect of suppressing breast cancer cell growth. In conclusion, our study dissects a mechanism underlying PRMT1-mediated RNA alternative splicing. Thus, PRMT1 has great potential as a therapeutic target in breast cancer treatment..
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124723013979